content
- HDD or SDD
- Physical size – 3.5 or 2.5 inches
- Bus type – ide or sata
- Bus generation
- Drive rotation speed
- Hard drive capacity
- Buffer memory size
- Heating temperature and power consumption
When choosing a hard drive, you need to take into account such parameters as its physical size (in inches), bus type (IDE or SATA), bus generation, drive rotation speed and, of course, capacity. Particularly sophisticated users can also pay attention to the volume of the buffer memory and the heating temperature. It is also worth distinguishing between HDD and SSD.
HDD or SSD
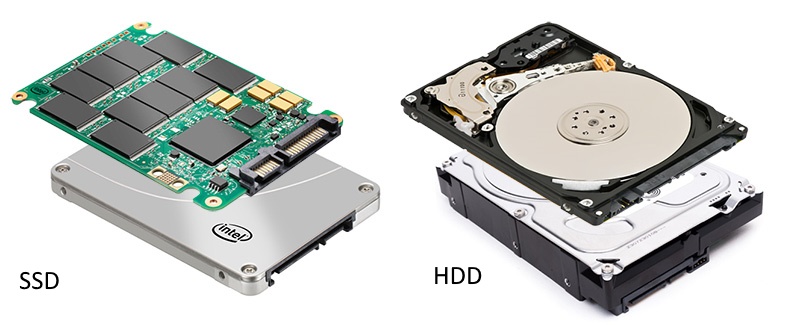
HDD (Hard Disc Drive) is the most common type of hard drive. These are traditional magnetic drives in which 'pancakes' with information recorded on them rotate. It is this mobility that leads to various problems, such as the appearance of bad sectors after mechanical impact on the case of a working disk or a sudden power outage.
SSD (Solid-state Drive) is a new type of hard disk that uses a recording technology similar to that used in flash drives. Nothing moves in them, so the risk of broken sectors appearing is quite small. However, SSDs are very expensive and have a short lifespan due to the limited number of rewriting cycles. But on the other hand, such disks work very quickly (their read / write speed is higher than that of HDD) and do not need defragmentation.
Thus, the following advantages of HDD over SSD can be distinguished:
- Low price, especially in terms of 'ruble per gigabyte';
- Long operational period, which, if all conditions are met, can be several years.
SSDs have the following advantages over HDDs:
- High speed of reading and writing;
- No need to defragment;
- File access speed (especially when reading / writing random sectors) does not decrease over time.
The optimal configuration is as follows. The operating system and the most important programs are installed on a small SSD, and user data is stored on a large HDD.
Physical size – 3.5 or 2.5 inches
Winchesters are available in two formats – 3.5 “and 2.5”. The former are intended for use in system units, the latter are usually inserted into laptops and external hard drives.
Technically, a 'laptop' hard drive can be installed in the system unit. However, this is not worth doing. Slides in the case, which fix the hard drive, protect it from vibration.
Bus type – IDE or SATA
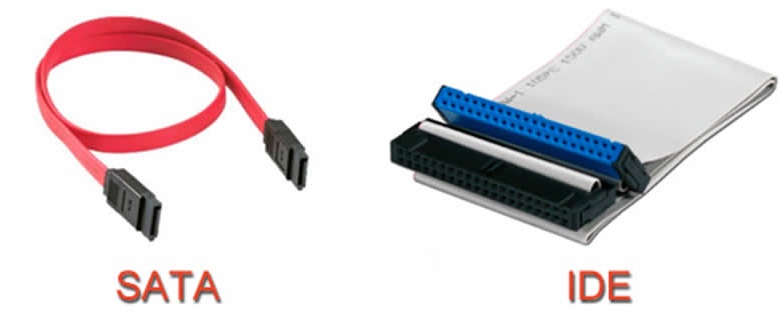
It should be noted right away that the IDE bus is practically not used now. Only very old computers and motherboards are equipped with it. However, on 'machines' that were released before about 2008-2010, this is the standard used, and there is simply no connector for SATA.
SATA is used in modern configurations. It provides faster data transfer rates (up to 6Gbps).
It should be noted that these connectors are not interchangeable. That is, you will not be able to connect an IDE drive to a computer with slots only for SATA, and vice versa. In case of urgent need, you can use special adapters, however, they greatly reduce the speed and do not differ in stability.
Bus generation
The SATA bus has existed in several generations (revisions). They are cross-compatible, so you can connect a SATA 1 hard drive to a motherboard equipped with a SATA 3 slot. Keep in mind, however, that the baud rate will be the same as that supported by the older standard.
That is, if you install a SATA 3 hard drive on a motherboard that only supports SATA 1, the baud rate will match SATA 1.
Likewise, if you plug a SATA 2 hard drive into a SATA 3 motherboard, the baud rate will match the SATA 2 speed.
The best solution would be to use a hard drive of the standard and generation supported by the motherboard.
Drive rotation speed
In hard disks such as HDD, special magnetic drives ('pancakes') are used to store information. In the course of their work, they rotate, and the read and write heads read and write data to them.
The rotation speed of the drives directly affects the performance of the hard drive. The higher it is, the faster the hard drive can find the stored information or free space for recording a new one. Most modern railway models have a rotation speed of 7200 rpm, which corresponds to a search time of 8.5 ms, and a total response delay of 12.7 ms.
There are also faster railways. For example, the WD Raptor has a rotational speed of 10,000 rpm. The seek time for this device is 5.5ms and the total latency is 8.5ms. The Seagate Cheetah at 15,000 rpm has a seek time of 3.8 ms and a total latency of 5.8 ms.
The total latency is a combination of the seek time and the time it takes for the hard drive to spin up the drives.
It should be noted that the speed of rotation determines the search time. If you need to read information from a large, sequential block of data, disks with different values of this parameter work approximately the same. Therefore, it is recommended to regularly defragment the hard drive.
Capacity

The capacity, which is measured in GB or TB, is important primarily for the user. It determines how much information can fit on the hard drive.
However, very cheap low-capacity models are not recommended. Firstly, the operating system Windows 'selects' 20-30 GB for its needs, and this volume only increases over time due to the appearance of new files. Secondly, even a web browser with active use in a week can 'eat off' 1 GB. Finally, the paging file is located on the hard disk.
In addition, the higher the hard drive capacity, the lower the cost of 1 GB. Therefore, for example, 750 GB and 1 TB drives differ in price slightly.
Buffer memory size
Buffer or cache memory is a type of random access memory. Unless it is used exclusively in the hard drive. In it, the hard drive stores various data that it reads from magnetic drives. It also contains information that most often requires access.
Therefore, the higher the cache memory, the faster the hard drive works. But this is only in theory. In practice, it turns out that there is no fundamental difference between models with 32 MB of cache memory and those with 64 MB. Therefore, it makes no sense to choose a hard disk drive with the maximum buffer – it is enough that it is simply large (16 or 32 MB for desktop configurations and 8 or 16 MB for laptops).
Heating temperature and power consumption
Like any other component of a computer, a hard disk drive heats up during operation. With a significant increase in temperature, it may stop functioning normally, which will lead to the appearance of broken or unreadable sectors.
Heat increases especially in configurations where several hard drives are used at once. The solution to this problem will be to install another cooler in the case, which will blow the array of hard drives.
If there is no room in the case for an additional cooler, then hard drives with low heating and power consumption are the solution. But it is worth remembering that their performance is also not very great.
Summary
When choosing a hard drive, you need to pay attention first of all to the characteristics of the computer motherboard – connection standard, generation, etc.
You shouldn't skimp on very cheap models with low rotational speed or low cache size. Very expensive ones are also unnecessary in most cases.
!
In the following articles, our experts will tell you how to choose an SSD drive and the secrets of choosing RAM for your computer.
Attention! This material is the subjective opinion of the authors of the project and is not a purchase guide.









