Review of the best according to the editorial board. On the selection criteria. This material is subjective and does not constitute advertising and does not serve as a purchase guide. Before buying, you need to consult with a specialist.
Correct diagnosis and treatment of bronchial asthma is a serious problem in modern pulmonology. Asthma is a multifaceted disease. On the one hand, this is a chronic inflammation of the bronchial tree, with an abundance of symptoms such as shortness of breath on exhalation, that is, expiratory dyspnea, various wheezing and coughing, a feeling of chest congestion.
Such symptoms appear from time to time, are of varying intensity, and are associated with an exacerbation of bronchial asthma, which in a typical form proceeds as an attack of suffocation, alternating with interictal periods.
Many patients with bronchial asthma have a pronounced relationship with allergies. This is the most common type of asthma and is identified as early as childhood. In such patients from a very early age, drug or food allergies, atopic dermatitis, and diathesis are determined. In the sputum of these patients, severe eosinophilia is found, and in those with the allergic type there is a good response to treatment with hormonal agents, especially in the form of inhalation. There are other types of bronchial asthma, which we will not dwell on here. This requires a long time, complex diagnostics, including spirometry, immunological and allergological studies.
- Asthma risk factors
- About planned and emergency asthma treatment
- Review of asthma medications
- Emergency therapy: treating asthma attacks
- Bronchodilators – inhaled beta-2 agonists: Salbutamol (Ventolin)
- Advantages and disadvantages
- AHP: Ipratropium bromide (Atrovent-N)
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Ipratropium bromide + fenoterol (Berodual, Astmasol, Inspirax)
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Adenosinergics: Theophylline (Teotard, Teopek)
- Advantages and disadvantages
- GCS: budesonide (Pulmicort, Benacort)
- Basic asthma treatment outside of attacks
- Leukotriene blockers: montelukast (Singular, Almont, Glemont, Montelar, Singlon, Ectalust).
- Inhalation hormones + β-2 agonist: Budesonide + formoterol, Symbicort Turbuhaler
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Xolar (Omalizumab) – monoclonal antibodies
- Spiriva (tiotropium bromide)
- Advantages and disadvantages
Asthma risk factors
However, in all cases, it is extremely important to determine those environmental factors that may be involved in the occurrence of bronchial asthma. In addition to allergens such as dust mites, animal dander, fungi, pollen, it is very important to identify infectious factors such as frequent viral diseases. Occupational hazards are important, as well as harmful volatile substances. These are tobacco smoke, sulfur dioxide, gasoline and diesel fuel combustion products.
Unhealthy diet appears to be a very important risk factor. Asthma patients typically eat a lot of foods that are as highly processed as possible and are low in antioxidants. Such patients eat little vegetables, fruits, fiber and fatty fish. But fast food, smoked meats, canned food prevail.
In the diagnosis of bronchial asthma in adults, it is very important to pay attention to the following symptoms, which significantly increase the likelihood of such a diagnosis. These are the following signs:
- the appearance of congestion in the chest;
- suffocation;
- cough, especially at night and early morning hours;
- provocation of such symptoms with cold air, physical activity or various allergens;
increased symptoms of choking and coughing after taking acetylsalicylic acid, or aspirin, beta-blockers, which are used to stop tachycardia and treat coronary heart disease;
- the presence of asthma or atopic diseases in relatives;
- a large number of dry, wheezing rales;
- low levels of spirography, such as peak expiratory flow;
- a large number of eosinophils in the peripheral blood.
Treatment of bronchial asthma is a stepwise process, and in all modern medicine there are five successive steps of treatment. What is the treatment?
About planned and emergency asthma treatment
Treatment of bronchial asthma (especially relapsing and mild asthma) begins with the first stage. If it is not effective, then therapy is intensified, and the patient is transferred to the second stage. In the same way, if the treatment at the second stage is ineffective, then gradually the drugs are replaced, other drugs are added, the doses are increased, and, in the end, a certain treatment regimen is selected for the patient.
After at this stage control over the course of bronchial asthma is established and the attacks are eliminated, the volume of treatment can be gradually reduced until the optimal minimum set of drugs is reached, in which either attacks do not occur at all, or they occur no more than once in Week. Such treatment of bronchial asthma is called the selection of basic therapy. It is carried out, selected, and optimized for a specific patient outside the state of seizures.
However, there is a second side to the treatment of bronchial asthma. This is actually the relief of an attack of bronchial asthma, which is carried out according to slightly different rules. This combination of the two sides of therapy – relief of an attack and treatment in the interictal period is the basis of modern therapy of bronchial asthma.
Consider the main drugs that are intended for emergency care and relief of the developed attack of bronchial asthma. It goes without saying that these drugs, selected together with a pulmonologist, should always be at the patient's hand in order to use them at any time of the day when alarming symptoms appear.
All drugs described in this material are not related to the rating, and their sequence is dictated only by the form of presentation of the material. The name of a medicinal product consists of the international non-proprietary name (INN). Then comes the name of the original drug, which was first launched on the market under its own name. Usually this is the most expensive means, the price 'flagship' of the line. The following are commercial copies, or generics. The price is usually given for the original product, in the range from the cheapest to the most expensive, and is relevant for pharmacies of all forms of ownership for August 2019 in the Russian Federation.
Review of asthma medications
| Nomination | a place | Name of product | price |
| Emergency therapy: treating asthma attacks | 1 | Bronchodilators – inhaled beta-2 agonists: Salbutamol (Ventolin) | 135 RUB |
| 2 | AHP: Ipratropium bromide (Atrovent-N) | 376 r | |
| 3 | Ipratropium bromide + fenoterol (Berodual, Astmasol, Inspirax) | 261 r | |
| 4 | Adenosinergics: Theophylline (Teotard, Teopek) | 135 RUB | |
| 5 | GCS: budesonide (Pulmicort, Benacort) | 844 RUB | |
| Basic asthma treatment outside of attacks | 1 | Leukotriene blockers: montelukast (Singular, Almont, Glemont, Montelar, Singlon, Ectalust). | RUB 1 601 |
| 2 | Inhalation hormones + β-2 agonist: Budesonide + formoterol, Symbicort Turbuhaler | 2 369 RUB | |
| 3 | Xolar (Omalizumab) – monoclonal antibodies | RUB 18,500 | |
| 4 | Spiriva (tiotropium bromide) | RUB 2,717 |
Emergency therapy: treating asthma attacks
First of all, you need to decide what an exacerbation, or an asthma attack, is. This is a condition in which the patient's cough gradually increases, wheezing increases, shortness of breath appears, and a symptom of chest congestion. It is important to remember that exacerbations can develop not only in a patient with an already diagnosed asthma, but also be the very first symptom of a newly emerging disease.
Any patient with this diagnosis can have an attack of bronchial asthma, regardless of its severity, even in patients with mild severity. A typical attack can develop at different rates, sometimes it takes several minutes to develop, and sometimes symptoms increase over a long time, even up to 2 weeks.
Resolution, or attenuation of an exacerbation, also requires a long time, from several days to the same 2 weeks. Exacerbation of bronchial asthma is a rather serious matter. It is known that in any hospital with an emergency department, about 12% of all admissions are attacks of bronchial asthma, and about 5% of those admitted with this diagnosis require immediate hospitalization in the intensive care unit.
Clear and understandable criteria for the severity of an attack are the respiratory rate, which in a severe attack exceeds 25 breaths per minute, an increase in the pulse rate, which, with the same severe attack, exceeds 110 beats per minute. An important diagnostic criterion is the inability to pronounce any sentence or phrase on one exhalation. In the event of a drop in blood pressure, the development of bradycardia, the appearance of cyanosis of the skin, or cyanosis, a drop in capillary oxygenation of less than 92% – we are talking about a life-threatening attack, and such a patient is hospitalized in the intensive care unit without fail.
How to treat exacerbation of bronchial asthma? First of all, this is the appointment of fast-acting bronchodilators, which are beta-2 adrenergic receptor agonists. Then – the use of anticholinergic drugs, as well as a combination of these two groups of drugs, which with a high level of evidence increase the speed of resolution of an asthmatic attack and significantly reduce mortality. Finally, the main intervention for the treatment of exacerbation may require the early use of glucocorticosteroids, both in the form of systemic administration and in inhalation, as well as oxygen therapy. Consider the main drugs used to relieve an attack of bronchial asthma.
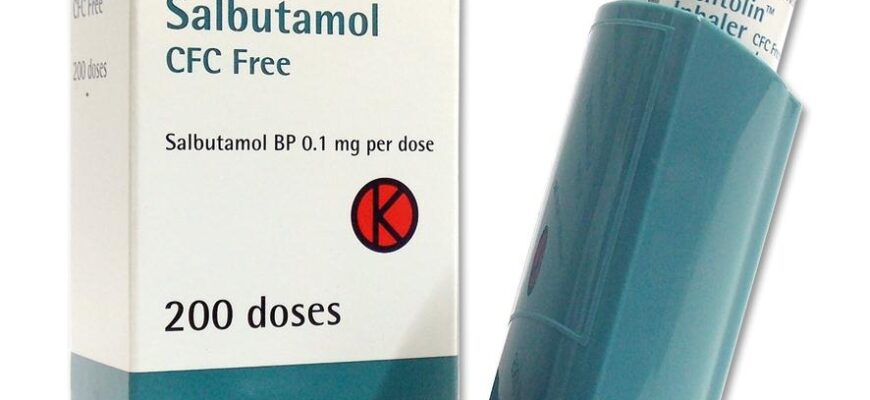
Bronchodilators – inhaled beta-2 agonists: Salbutamol (Ventolin)
Popularity rating: 4.9
Agonists of β-2 adrenergic receptors, used in nebulization or inhalation form, are the most economical and optimal method of managing patients with bronchial asthma in the presence of a mild or moderate attack.
Ventolin affects the adrenergic receptors of the smooth muscles of the bronchial tree (β-2), and does not affect similar myocardial receptors, which are called β-1. This leads to a pronounced expansion of the bronchi, which relieves an attack of bronchial asthma. The use of salbutamol-Ventolin in particular reduces the air resistance of the airways, increases the vital capacity of the lungs, and activates the ciliated epithelium. This leads to improved secretion and mucus production, which is very important for the prevention of respiratory infections.
Inhaled forms of salbutamol act very quickly: the onset of the effect develops after 5 minutes, and after another 5 minutes, the effect increases to 75% of the maximum, and the duration of action is up to 6 hours. However, this drug must be used more than once, and strictly follow the instructions of the attending pulmonologist. Ventolin is shown, first of all, for stopping an attack, and then for a prophylactic purpose, in order to prevent an attack of bronchospasm, for example, when a known allergen enters the body, when exposed to frosty air, or during physical exertion, when an attack has already occurred in similar conditions . It is also possible to use salbutamol in complex therapy, not only in the presence of exacerbations, but also for long-term treatment of bronchial asthma in the interictal period.
Bronchodilators should be used quite often. But in the case of Ventolin, the manufacturer does not recommend using it more often than 4 times a day. The recommended dose for relieving an attack of bronchial asthma is usually one or two inhalations, that is, from 100 to 200 g of salbutamol.
Ventolin is produced by Glaxo Wellcom, in an aerosol can for metered inhalation. One spray dose accounts for 100 μg of salbutamol, one aerosol can is designed for 200 doses. The cost of one package is from 107 to 136 rubles.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of all inhaled short-acting β2-receptor agonists are a quick effect, the ability to use it for prophylactic purposes, and the ability to prescribe them for obstructive bronchitis without a diagnosis of bronchial asthma. This drug is included in the list of vital and important drugs (VNCD), and therefore is inexpensive. However, Salbutamol and its analogs must be inhaled several times, and there are contraindications to the use of salbutamol in children under two years of age. Despite the selectivity (selectivity) of the action, the drug is used with caution in various cardiac pathologies, thyrotoxicosis, pregnancy, breastfeeding, as well as in decompensated diabetes mellitus. There are also various drug interactions.
AHP: Ipratropium bromide (Atrovent-N)
Popularity rating: 4.8
Anticholinergic drugs (ACP) are derivatives of atropine, their function is to block specific cholinergic receptors of bronchial smooth muscles. As a result, the mucous membrane of the bronchi dries up, the secretion of the mucosa decreases due to inhibition of the effect on the bronchial glands. Anticholinergic drugs effectively expand the bronchi, and prevent their narrowing, especially due to the influence of cold air, cigarette smoke, relieve spasm associated with the parasympathetic effects of the X pair of cranial nerves. One of the most important representatives of this class of drugs used to relieve an attack of bronchial asthma is ipratropium bromide (Atrovent-N). The effect of expansion of the bronchi develops within 10 minutes, the maximum development after 2 hours, and the duration of action – up to 6 hours.
Atrovent-N is used to relieve attacks of mild to moderate bronchial asthma. It is especially recommended to use Atrovent-N if the patient has concomitant damage to the cardiovascular system. It is also indicated for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. It is necessary for adults to use Atrovent-N in the form of an aerosol, 2 doses up to 4 times a day, and in the event of an attack of bronchial asthma, the dose can be increased up to 12 times a day. However, all this must first be agreed with the doctor.
The aerosol metered for inhalation of Atrovent-N contains 200 doses in a 10 ml canister, each dose contains 20 micrograms of ipratropium bromide. Atrovent-N is produced by the German company Boehringer Ingelheim, and the cost of one cylinder ranges from 300 to 380 rubles.
Advantages and disadvantages
The big plus of Atrovent is the absence of an overdose. In order to really poison the body with ipratropium, you must immediately inhale about 500 doses. The systemic effects associated with anticholinergic symptoms are therefore very weakly expressed, and that is why the remedy is recommended, including for patients with cardiovascular pathology. They do not develop tachycardia, urinary retention, palpitations, dry skin and mucous membranes characteristic of atropine exposure. However, in some cases, patients may experience coughs, hives, and allergic reactions. If the patient has an attack of suffocation very quickly, then first of all it is necessary to use salbutamol, and secondly – Atrovent, since the effect of bronchial expansion is more likely to develop in beta-adrenergic receptor stimulants, and only then in Atrovent and its analogues.
Ipratropium bromide + fenoterol (Berodual, Astmasol, Inspirax)
Popularity rating: 4.7
In order not to use alternately salbutamol and ipratropium bromide, and not to carry them in different pockets, a drug was created, so to speak, in one bottle, combining β2 – an adrenergic agonist and an atropine derivative. Only instead of salbutamol, its analogue, fenoterol, was taken. This combination can provide a more persistent and pronounced effect of bronchodilation and elimination of an asthmatic attack than the separate use of these drugs. The combination of these funds at the prehospital stage leads to a decrease in the number of hospitalizations of patients, since an improvement in well-being occurs even before the arrival of an ambulance.
Berodual can also be used for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, in the presence of emphysema, and even in the second and third trimester of pregnancy. Inhalation of Berodual in adults in case of an acute attack of bronchospasm can be from 1 ml, or 20 drops to 50 drops, or 2.5 ml. The lowest recommended dose, that is, 20 drops, is diluted with isotonic sodium chloride solution to 4 ml and is completely inhaled using a nebulizer.
Berodual is produced by the German company Boehringer Ingelheim, and one bottle of solution for inhalation, in 20 ml, designed for 20 minimum doses, is sold in pharmacies at a price of 230 to 270 rubles.
Advantages and disadvantages
Plus Berodual is a proven improvement and decrease in hospitalizations, a more beneficial pharmacoeconomic profile (two in one), and a low price. The disadvantage is the need to use a nebulizer, preliminary dilution with isotonic solution, as well as some symptoms associated with an overdose of fenoterol. These are palpitations, tremors, changes in blood pressure, hot flashes, or a feeling of heat.
Adenosinergics: Theophylline (Teotard, Teopek)
Popularity rating: 4.6
The bronchodilator effect of theophylline occurs due to blocking of phosphodiesterase, binding of receptors to adenosine and relaxation of the muscles of internal organs. At the same time, it increases the tone of the respiratory muscles, that is, the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, increases the supply of oxygen to the blood, that is, increases its oxygenation, and dilates the vessels of the lungs. Theophylline is used for bronchial asthma, pulmonary emphysema, obstructive bronchitis, and status asthmaticus.
At present, Theophylline and its analogs are widespread in developing countries, and in countries with a high level of medicine, Theophylline was for some time in second-order drugs, it was replaced by modern beta-2 agonists and anticholinergics. But now theophylline is gradually returning to the system, and it is used to treat exacerbations of bronchial asthma and in the interictal period.
Teotard is produced in the form of retarded capsules, that is, with sustained release, which provide a uniform and long-term effect. One package of 40 tablets of 350 mg each will cost from 220 to 420 rubles. Teotard is produced by the Slovenian company Krka. It can be used after meals, for adults one tablet 1 time per day in the evening, if treatment is started, and the maintenance dose is twice as much, twice a day. In the course of treatment, the dose must be adjusted according to the definition of theophylline in the blood serum.
Advantages and disadvantages
Theophylline has complex effects on pulmonary circulation and smooth muscle, but at the same time it can cause seizures, anxiety, nasal congestion, nausea and vomiting. It interacts with many medicinal substances, possibly overdose symptoms. An obvious disadvantage is the need to regularly determine the concentration of theophylline in the blood serum, so only a doctor should prescribe this drug.
GCS: budesonide (Pulmicort, Benacort)
Popularity rating: 4.5
Previously, patients who, with the help of β2-receptor agonists and other bronchodilators, failed to stop an attack of bronchial asthma, were prescribed glucocorticosteroid hormones, moreover, in a systemic manner, most often by intravenous route. Usually, dexamethasone was administered at home, by ambulance, and in the pulmonary or emergency department, patients were injected with the same dexamethasone. If the hospital was richer, then methylprednisolone. Prednisolone was then given in tablets after the attack had stopped.
At the same time, both intravenous and oral routes are equally effective in exacerbating bronchial asthma, but, naturally, the tablets simply do not have time to act in case of a sudden onset of an attack. Prednisolone was prescribed for a week, in tablets, after the infusion was stopped. However, there are also inhaled corticosteroids – drugs that are used with metered nebulizers, nebulizers, and are not inferior to infusions and injections of glucocorticosteroid hormones. In some cases, they even surpass them in the speed of onset of the effect and in the safety profile.
One of these drugs is budesonide, or Pulmicort. In addition to relieving attacks of bronchial asthma, it is used in acute obstructive laryngitis, is available in suspension, and is indicated for both long-term treatment of bronchial asthma and for relief of attacks. It must be used individually, up to 4 mg per day for adults, for maintenance therapy. In case of exacerbations, the dose is increased, but always by prior agreement with the pulmonologist. Pulmicort Turbuhaler is produced by Astrazeneca from the UK, and powder for inhalation in the amount of 100 doses at the rate of 200 mg per dose costs from 400 to 750 rubles.
Basic asthma treatment outside of attacks
Above, it was already mentioned about the stepwise treatment of bronchial asthma in a planned manner, when we are not talking about attacks. Since the first stage uses the same drugs as for the relief of seizures, that is, β2-receptor agonists and their combination with ipratropium bromide, low doses of inhaled corticosteroids, and they are also present in other stages of more serious treatment, then we are at we will not dwell on them. You will only consider those more powerful and modern drugs that appear in more advanced stages of treatment. At the second stage, antagonists of leukotriene receptors appear. What are these drugs?
Leukotriene blockers: montelukast (Singular, Almont, Glemont, Montelar, Singlon, Ectalust).
Popularity rating: 4.9
The active substance montelukast sodium belongs to bronchodilators, but only to blockers of special receptors, which are called leukotriene. Their blockade makes it possible to interrupt chronic inflammation, which constantly maintains the bronchi in an anxious, hyperreactive state in this disease. As a result, the spasm of the smooth muscles of the bronchi decreases, the migration of active leukocytes, such as macrophages and eosinophils to the lungs, decreases, the secretion of mucus and inflammatory immunoglobulins of the secretory series also decreases.
The drug is highly active when taken orally, and after a single dose, the effect persists for a long time. Montelukast (Singular) is used for long-term treatment of bronchial asthma, including its aspirin form, as well as for the prevention of bronchospasm attacks. In some cases, this drug and its analogues are indicated for the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis, hay fever, that is, hay fever. It is necessary to use the drug in the dosage indicated by the doctor. However, according to modern data, nevertheless, inhaled corticosteroids are drugs that show higher efficiency in the second stage of treatment than the leukotriene receptor antagonists prescribed instead.
It is clear that long-term, planned therapy of bronchial asthma may not include very fast-acting drugs, so you can get by with pills, and even chewable tablets. So, the drug Singular is produced by the well-known pharmaceutical company Merck Sharp and Dome in a dosage of 4 mg per tablet, and 5 mg per tablet. It will cost from 1400 to 1700 rubles for a pack of 28 tablets of 5 mg each.
Inhalation hormones + β-2 agonist: Budesonide + formoterol, Symbicort Turbuhaler
Popularity rating: 4.8

Moving further along the stages of treatment of bronchial asthma, we find a combination of an inhaled glucocorticosteroid drug together with a bronchodilator fenoterol, which is similar in its action to salbutamol. One of the most highly effective, but at the same time expensive means, Symbicort Turbuhaler can be considered.
Symbicort should be prescribed to patients at least 6 years old, with special care it should be used against the background of pulmonary tuberculosis, various respiratory infections, diabetes mellitus and other diseases. This drug is indicated, of course, not for emergency relief of seizures, but exclusively for routine treatment, and it is effective in reducing the frequency and severity of exacerbations. However, some experts believe that this drug can be successfully used to relieve seizures, but whether it is worth doing it or not, you need to consult with your doctor. It has been proven that the combined effect of budesonide and fenoterol is higher than the separate administration of these drugs, and a decrease in the frequency of exacerbations of the disease, an increase in lung function and the elimination of symptoms of bronchial asthma are also more pronounced compared to the separate use.
Symbicort should be used at higher stages of treatment, and it is not intended to start treating asthma with it for the first time, and especially mild asthma. Usually, before a patient is prescribed Symbicort, he has already undergone beta-adrenomimetics, ipratropium bromide, and isolated hormonal drugs, and all this did not achieve its goal. The patient may have even taken leukotriene antagonists. The selection of the dose is a matter of the attending pulmonologist, it should be the smallest, but, nevertheless, the doctor and the patient must control the symptoms of bronchial asthma against the background of this small dose, preventing exacerbations.
At the beginning of therapy in adults, the use of no more than two inhalations per day is indicated, and under special conditions, by mandatory agreement with the attending physician, no more often than eight inhalations per day. Having determined the really healing dose, it is necessary to slowly and gradually try to remove the number of daily inhalations, decreasing them by one. The ideal option is one dose once a day, with the subsequent possible withdrawal of this serious remedy.
This highly active combination drug is produced by Astrazeneca from the UK, and one bottle of powder for inhalation, designed for 120 doses at the rate of 160 micrograms of the hormone and 4.5 mcg of the bronchodilator fenoterol, will cost from 2,000 to 2,700 rubles. The drug has analogues that are much cheaper, in the same dosage and in the same bottle from only 860 rubles.
Advantages and disadvantages
Like any hormonal drug, Symbicort has its drawbacks, in particular, immunosuppressive action. Quite often, from its use, headache, palpitations and tremors occur, and due to a decrease in immunity with prolonged use, there may be thrush, or candidiasis of the oral mucosa and pharynx. These side effects develop quite often, from 1% to 10% of all patients. Also, this drug has a rather high cost, but the best quality. During pregnancy, it is better not to use this remedy, but to use it only if the benefits of using the drug are higher than the possible risk to the unborn child.
Xolar (Omalizumab) – monoclonal antibodies
Popularity rating: 4.7
Finally, the crown of modern drug therapy, as in the case of many other diseases (psoriasis, multiple sclerosis), is the expensive treatment with recombinant humanized monoclonal specific antibodies. There is also a remedy for asthma. This drug has a pronounced immunosuppressive effect, and is indicated exclusively for patients with an allergic type of bronchial asthma, which is also called atopic. Roughly speaking, Xolar binds to immunoglobulins E and eliminates the flow of reagin-mediated allergic reactions. Free immunoglobulin E becomes scarce, the cascade of allergic reactions does not start, and therefore an attack of bronchial asthma either does not occur, or proceeds much easier.
This drug is indicated for the routine treatment of severe allergic bronchial asthma, especially if it is impossible to control the condition using hormonal drugs, that is, in patients with unpredictable attacks. The second indication is the treatment of severe forms of idiopathic urticaria, which cannot be treated with an antiallergic agent.
Xolar is prescribed in subcutaneous injections, in no case should it be administered intramuscularly or intravenously. The methods of administration and doses are subject to special calculations, which are not carried out here. However, it should be said that the drug is administered once subcutaneously every month, or every 2 weeks, depending on the initial concentration of immunoglobulins E in the blood plasma and depending on the patient's body weight. So, if the patient has a mass of 80 kg, and the concentration of immunoglobulins E is higher than 400 units per ml, then he is prescribed 300 mg of the drug subcutaneously after 2 weeks.
On average, the effect of the treatment appeared after 4 months, and this remedy is recommended for long-term therapy. If you cancel it, then immunoglobulin E rises again, and the severity of bronchial asthma increases again. The effect of the use is a more rare development of seizures, less need for emergency care, relief of the course of seizures and improved well-being in the interictal period.
It is important to remember that Xolar is not intended for the relief of acute attacks or the treatment of status asthmaticus. Here the advantages and disadvantages, overdose, and side effects are deliberately not given, since the instructions for the use of the drug are a multi-page book, it must either be studied in great detail, or not use the tool at all.
It remains to inform about the price of this drug produced by Novartis Pharma. Like all monoclonal antibodies, they require a very complex technological cycle, and therefore the drug is very, very expensive for Russians. A bottle of lyophilisate for the preparation of a concentrate in an amount of 150 mg will cost an average of 20,000 rubles in pharmacies. Accordingly, a dose of 300 mg will cost the patient 40,000 rubles, and the monthly cost of treatment will be 80,000 rubles. If we consider that Xolar is a means for long-term therapy, then the cost of treatment during the year will be 960 thousand rubles, which is equal to the cost of the new domestic SUV UAZ Patriot.
Spiriva (tiotropium bromide)
Popularity rating: 4.6
Finally, in conclusion of the review of drugs used in severe bronchial asthma, at the fifth stage of treatment, consider the drug Spiriva, or tiotropium bromide. This drug is produced by the German company Boehringer Ingelheim, it is produced in the form of capsules with powder for inhalation, each capsule contains 18 μg of tiotropium. Such a package of 30 capsules, which is sold together with the inhaler, will retail from 2,200 to 2,700 rubles.
What is this drug? It is recommended to prescribe it additionally at the fifth stage of therapy, to all patients with bronchial asthma, in whom, despite all the correct treatment, it is severe, and patients are already on high doses of inhaled corticosteroids. It is possible that these patients are also already receiving monoclonal antibodies, so tiotropium, despite its relatively high price, seems economically insignificant compared to the previous drug.
What is this remedy? It is an anticholinergic against muscarinic receptors, which has a long-term effect. The blockade of specific muscarinic receptors will result in a pronounced relaxation of smooth muscles, or a bronchodilating effect, which is dose-dependent, but lasts for at least a day.
Taking this drug increases the spirogram indicators within half an hour after a single dose, and this effect lasts a day. Spiriva reduces shortness of breath, exercise tolerance, the number of exacerbations and, as a result, significantly improves the patient's quality of life. It is reliably known that during treatment with this drug, the risk of death decreased by 16%, which is a lot. This drug is indicated exclusively as a maintenance therapy, and in no case should it be used as a means to stop an exacerbation. Spiriva is available for inhalation use, one capsule per day at the same time.
Advantages and disadvantages
Improving the quality of life, improving the course of the disease, reducing symptoms, lowering overall mortality by 16% are excellent data, and the drug is extremely useful. But at the same time, you should still remember that you need to use the inhaler correctly, have specific skills, and in case of an overdose, dry mouth and eyes may appear, and conjunctivitis may develop. In no case should Spiriva be used at the very beginning of treatment, for milder forms of bronchial asthma, and should not be used for emergency treatment of attacks. It should be remembered that the remedy should not be used in the first trimester of pregnancy, in children under 18 years of age, and special care must be taken when prescribing Spiriva in patients with glaucoma, prostatic hyperplasia (adenoma) or obstruction of the bladder neck in order to avoid difficulty urinating.
The popularity rating is based on the analysis of demand data from the wordstat.yandex.ru service.
Attention! This rating is subjective and does not constitute an advertisement and does not serve as a purchase guide. Before buying, you need to consult with a specialist.