Review of the best according to the editorial board. On the selection criteria. This material is subjective and does not constitute advertising and does not serve as a purchase guide. Before buying, you need to consult with a specialist.
In the night sky, the stars seem to be distant, twinkling lights, very tiny. But this is not the case. Stars are huge balls of incandescent matter that explode every second with thermonuclear reactions, and therefore shine so brightly that their rays reach our planet from the very depths of the Universe.
And the stars can be really huge. So much so that even the Sun next to them seems like a grain of sand. And in this material, we have collected the 10 largest stars in the Universe.
- Rating of the largest stars in the universe
- 10th place: Mu Cephei (1260 solar radii)
- 9th place: V766 Centauri (1315 solar radii)
- 8th place: AH Scorpio (1411 solar radii)
- 7th place: KY Swan (1420 solar radii)
- 6th place: VX Sagittarius (1520 solar radii)
- 5th place: Westerland 1-26 (1530 solar radii)
- 4th place: RW Cephei (1535 solar radii)
- 3rd place: WOH H64 (1540 solar radii)
- 2nd place: VY Big Dog (1540 solar radii)
- 1st place: UY Shield (2100 solar radii)
Rating of the largest stars in the universe
| Nomination | a place | star | diameter |
| rating of the largest stars in the universe | 10 | Mu Cephei | 1260 SOLAR RADIUS |
| 9 | V766 Centauri | 1315 SOLAR RADIUS | |
| 8 | AH Scorpio | 1411 SOLAR RADIUS | |
| 7 | KY Swan | 1420 SOLAR RADIUS | |
| 6 | VX Sagittarius | 1520 SOLAR RADIUS | |
| 5 | Westerland 1-26 | 1530 SOLAR RADIUS | |
| 4 | RW Cephei | 1535 SOLAR RADIUS | |
| 3 | WOH H64 | 1540 SOLAR RADIUS | |
| 2 | VY Big Dog | 1540 SOLAR RADIUS | |
| 1 | UY Shield | 2100 SOLAR RADIUS |
10th place: Mu Cephei (1260 solar radii)
Rating: 4.1
Mu Cephei is a red supergiant located in the constellation Cephei. Differs in extremely high brightness (apparent magnitude is up to +3.5), as a result of which it can be observed with the naked eye. It was discovered back in 1780-1783 by the German astronomer William Herschel.
It was he who described the light of Mu Cephei as a deep red. Therefore, it is also periodically called the 'Herschel garnet star'.
It is worth noting that Mu Cephei is an extremely unstable star. As a red supergiant, it constantly changes its luminosity, brightness, and even hue. Therefore, in some periods it is easy to replace it in the night sky, while in others it is necessary to peer. So, the apparent stellar magnitude varies from +3.4 to +5 with a period of 2 to 2.5 years.
Such instability suggests that the life cycle of Mu Cephei has come to an end. She had already completely burned all hydrogen in thermonuclear reactions and began to 'destroy' helium. Over the course of several million years, it can explode into a supernova and turn into a black hole.
Mu Cephei is 1260 times larger than the Sun and is located more than 5200 light years from us.
9th place: V766 Centauri (1315 solar radii)
Rating: 4.2
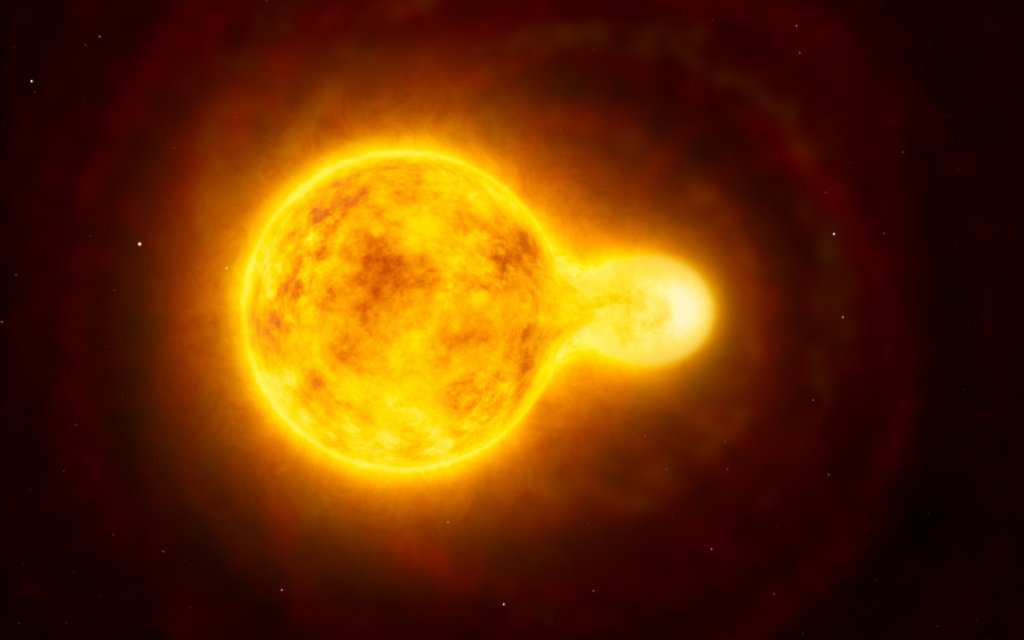

V766 Centauri (HR 5171 A) is the largest star in the constellation Centaurus. Interestingly, it is a double yellow supergiant, that is, in terms of its spectral characteristics (the type of thermonuclear reactions taking place and the glow temperature) it is similar to our 'yellow dwarf'. True, it has a companion – the small star HR 5171 B rotating at a close distance.
The companion star rotates so close to V766 Centauri itself that it practically touches its surfaces. It is very small compared to its 'neighbor', about 48 times smaller, but still not attracted by the gravitational field of HR 5171 A. The companion star orbits V766 Centauri with a period of 1300 'present' days.
V766 Centauri is 1,315 times larger than the Sun, shines bright yellow, and lies 11,700 light-years away. Has an apparent magnitude of +6.51, it can be observed with the naked eye.
8th place: AH Scorpio (1411 solar radii)
Rating: 4.3
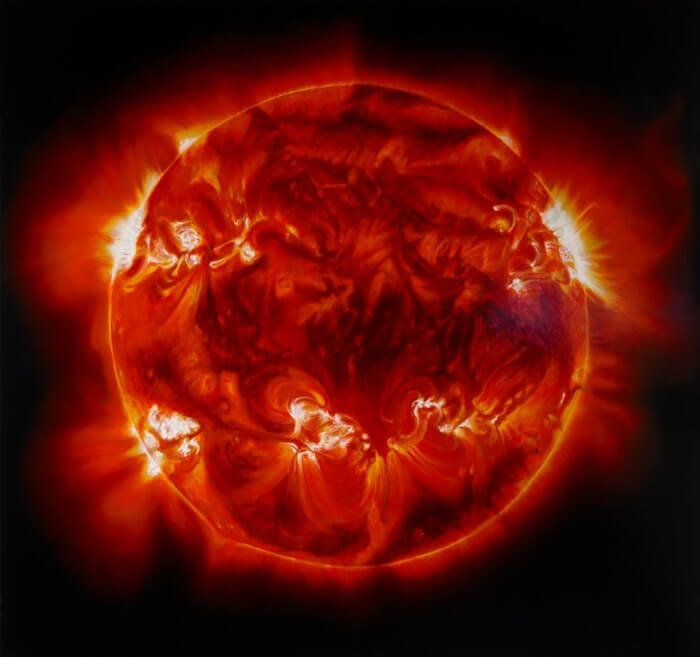

AH Scorpio is the largest star in the constellation Scorpio, a dying red supergiant. It is coming to the end of its evolution, even helium has practically depleted. So we can expect that soon AH Scorpio will explode into a supernova.
AH Scorpio has a low glow temperature of about 3700 K. The star is surrounded by a cloud of dust and gaseous oxygen with traces of silicon and even water vapor, which additionally absorbs the glow. Therefore, it is almost impossible to see it with the naked eye – the brightness is only from +9.6 to +6.5. As a result, it will be possible to see it only with very weak sky illumination and on cloudless nights.
AH Scorpio is enormous – it is 1411 times larger than the Sun. At the same time, it shines with a faint red light and is located at a distance of 7400 light years from us.
7th place: KY Swan (1420 solar radii)
Rating: 4.4
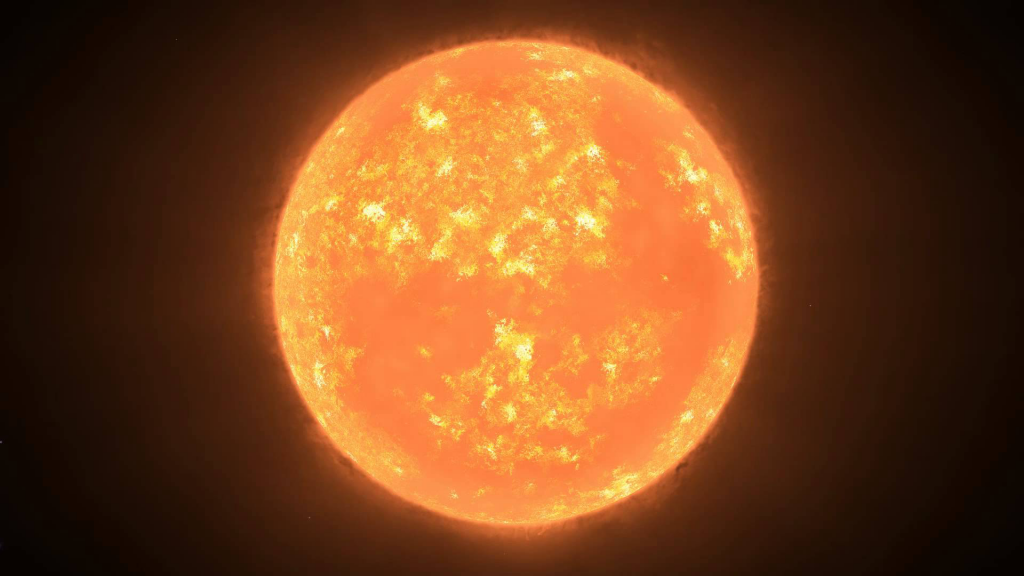

Cygnus KY is another dying red supergiant, the largest star in the constellation Cygnus. Despite its impressive size, it is invisible without a telescope. This is due to the fact that KY Cygnus is at the final stage of stellar evolution and may well explode as a supernova in the near future.
KY Cygnus is a gaseous dying star. It almost completely burned out the 'fuel' and therefore, despite its huge size, it is distinguished by its low mass. The outer shell is gaseous and highly rarefied. Due to the low density, problems arise with determining the exact size – it is not clear where the distinction between stellar and interstellar gas is located. Therefore, some researchers overestimate its diameter.
KY The swan is 1,420 times larger than the Sun and about 25 times heavier. Moreover, its apparent stellar magnitude is only +10.57, that is, it will not be possible to see it without using a telescope or other special equipment. The star shines with a faint red light with a temperature of 3500 K and is located just over 5100 light-years from us.
6th place: VX Sagittarius (1520 solar radii)
Rating: 4.5

VX Sagittarius is interesting not only for its size, but also for its 'behavior'. It is a 'pulsating' star that gets bigger and smaller over time. This behavior is due to the fact that VX Sagittarius is about to explode like a supernova – it has already burned almost all the 'fuel' in thermonuclear reactions.
However, VX Sagittarius is exposed to the stellar wind, which still has not exploded. The substance from its core constantly flows out into the surrounding space. As a consequence, VX Sagittarius is a very light star, and its outer shell consists of rarefied gas.
However, it is very bright – one of the brightest red supergiants. But it is impossible to see it with the naked eye. Its apparent magnitude ranges from +14 to +6.5, so observation will require the use of a telescope or similar equipment.
VX Sagittarius is on average 1,520 times larger than the Sun and about 12 times heavier, shines with a bright red light with a temperature of 3575 K, and is about 5,300 light-years away.
5th place: Westerland 1-26 (1530 solar radii)
Rating: 4.6
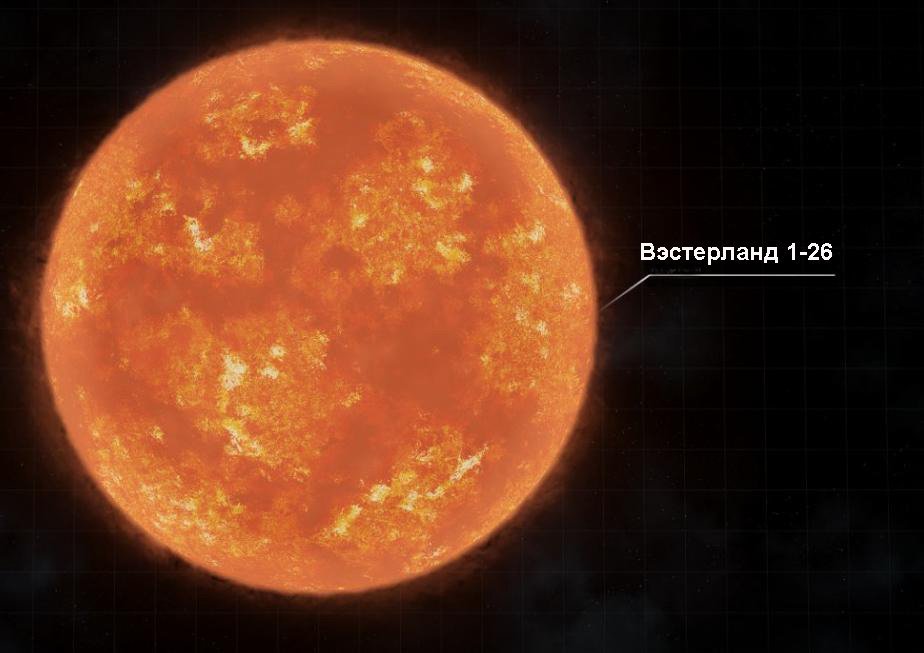
The red supergiant Westerland 1-26 is located in a cluster of stars in the constellation Altar. It is located too far away from us, therefore it is not well studied. Even the Westerlund 1 star cluster itself was discovered only in 1961.
Westerland 1-26 is the largest star in this cluster. It is a red supergiant, although according to some research data it even deserves to be called a hypergiant. This is due to the peculiarities of the space in which it is located.
So, around Westerland 1-26 is a huge cloud of ionized hydrogen, which is not only 'stellar fuel', but also capable of influencing the glow and spectral characteristics of radiation. Therefore, it is not possible to accurately determine the dimensions of the star.
According to the most reliable data, Westerland 1-26 is 1530 times larger than the Sun. It shines in a bright red color with a temperature of 3600 K and is 11,500 light-years away.
4th place: RW Cephei (1535 solar radii)
Rating: 4.7
RW Cepheus is a semi-regular variable red hypergiant, the largest star in the constellation Cepheus. It is at one of the final stages of evolution, as a result of which it constantly changes its physical size and degree of luminosity. Therefore, it is not possible to accurately determine its dimensions.
However, RW Cephei has a pretty interesting future. At the current evolutionary stage (red hypergiant), it has an unusually large size and, at the same time, an extremely small mass, which is 40 solar. Therefore, when it explodes, it can turn into a hypernova – a much brighter flash than a supernova – and a black hole.
According to the most reliable measurements, the RW of Cephei is 1535 times larger than the Sun. This star shines with bright red light with a temperature of 4015 K, but has a magnitude of +6.52 – that is, it will be difficult to find it with the naked eye. RW Cephei lies 11,500 light years away.
3rd place: WOH H64 (1540 solar radii)
Rating: 4.

WHO H64 is not in our galaxy, but in the neighboring one – in the Large Magellanic Cloud. The distance from this star to planet Earth is an impressive 163,000 light years. But this WOH H64 is a completely familiar red supergiant, which, however, rotates quite quickly.
Due to the rotation around this star, a gas and dust cloud of a rather unusual shape was formed – this is not a standard sphere, but a torus (something like a 'donut'). It partially blocks the red light of WOH H64, as a result of which its brightness is slightly lower than the calculated one. Nevertheless, this behavior of the red supergiant shows that the star is at one of the final stages of its evolution and that an explosion followed by transformation into a supernova will occur within several tens of thousands of years.
WOH H64 cannot be seen without a telescope, since its magnitude is only +9.69. The main observations of this red supergiant were carried out at the Chilean VLT laboratory.
According to calculations, WOH H64 is 1540 times larger than the Sun.
2nd place: VY Big Dog (1540 solar radii)
Rating: 4.

VY Canis Majoris is one of the largest stars in our galaxy. It is a traditional gas hypergiant, that is, it has colossal dimensions, but at the same time a relatively small mass. Thus, it is only 11-25 times heavier than the Sun.
VY Canis Majoris is a bright star visible in the night sky. Its apparent magnitude varies from +9.6 to +6.5, so it can only be seen with the 'armed' eye. This is exactly what the French astronomer Joseph Jerome de Lalande did back in 1801. For more than 200 years of observation, this red hypergiant has managed to change the shade of the glow – from crimson to burgundy, which indicates a rapidly proceeding evolution.
However, it is difficult to determine the exact size and characteristics of this star. VY Canis Majoris is surrounded by a cloud of gas and dust that obstructs observation. In addition, it periodically flares up, throwing a huge amount of matter into the surrounding space. And finally, it is extremely thin, on its 'surface' the gas is even more rarefied than in the Earth's atmosphere, so it becomes difficult to determine the 'end of space and the beginning of a star'.
Astronomers agreed that VY of Canis Major was tentatively estimated to be 1,540 times larger than the Sun. And it is located at a distance of about 3900 light years from our planet.
1st place: UY Shield (2100 solar radii)
Rating: 4.
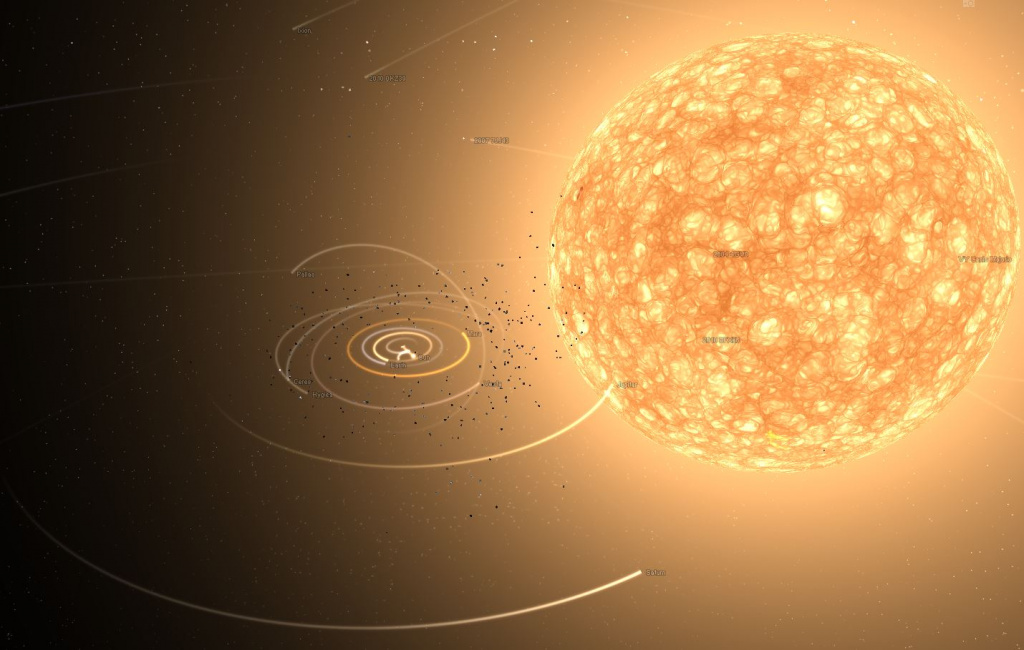

UY Shield is a red hypergiant, the largest currently known star in our galaxy (Milky Way). It is 2,100 times larger than the Sun! But at the same time, like many other gas hypergiants, it is very light. The mass of the UY Shield is estimated at 7-10 solar – and its density is even less than that of the Earth's atmosphere.
UY Shield has been known for a long time. It was first entered into stellar catalogs back in 1860, and this was done by astronomers from the Bonn Observatory. It can only be seen with the 'armed' eye – but powerful binoculars or a fairly simple telescope will suffice. UY Shield is located in the constellation of the same name, along the main beam of the Milky Way.
The apparent magnitude is +11.2. But this is primarily due to the fact that between us and the red hypergiant is a huge amount of interstellar dust. It is she who blocks the light from this impressive star.
UY Shield shines with a bright red light with a temperature of 3365 K. According to studies in 2018, such a small mass is due to the high rate of combustion of matter. But in the end, it shines very, very brightly – if it were not for interstellar dust, it would be the 5th most visible object in the sky.
UY Shield is located about 9500 light-years from planet Earth.
Attention! This rating is subjective and does not constitute an advertisement and does not serve as a purchase guide. Before buying, you need to consult with a specialist.








